Cross-hole Seismic
Principle
Cross-hole Seismic measurement is carried out in two wells, using excitation and reception systems that can adapt to the underground environment, to measure the primary wave velocity profile between two wells from the surface to the bottom. Based on the primary wave velocity profile and borehole data, general geology can be identified between the two wells such as geological stratification, fault zones, voids, isolated rock and so on.
The seismic wave is triggered in one borehole and received in the other borehole at regular depth intervals. The velocity of the signal travelling between them is derived with tomography.
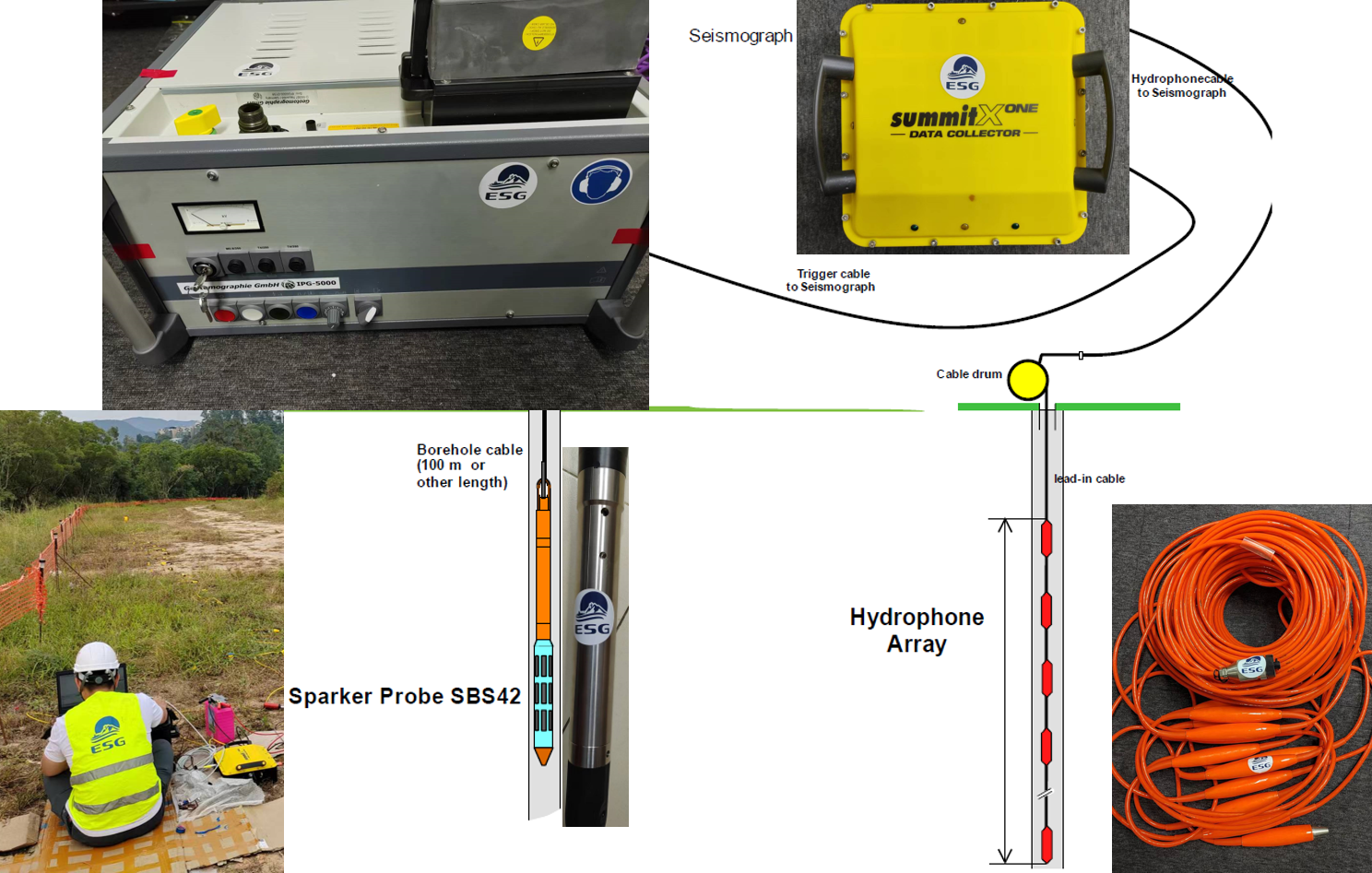
Applications
1.Geological Stratification
2.Fault Zones
3.Voids
4.Isolated Rock

